The external female* sex organs are collectively called the vulva, including the clitoris, clitoral hood (prepuce), labia (majora and minora) and the vagina.
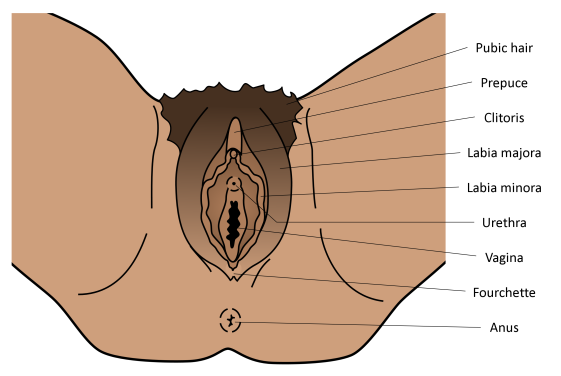
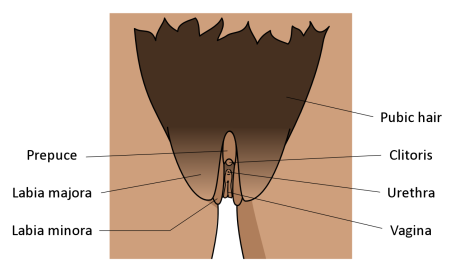
As with most body parts, the shape and size can vary a lot, so just because your vulva or someone else’s looks different to this, doesn’t mean it isn’t normal! There is a very interesting art project by Jamey McCartney on this topic called “The Great Wall of Vagina” which shows just how much this varies – you can check it out here.
The vulva and its connected internal organs are used for sex and reproduction and also for urination, via the urethra.
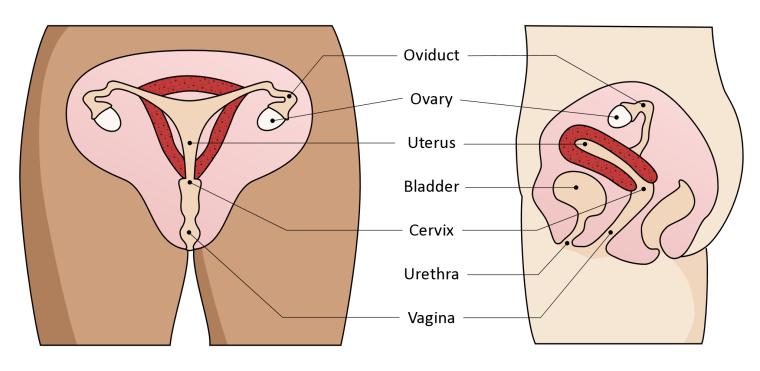
About once a month, one or two eggs are released from the woman’s ovaries, and travel down the fallopian tubes (also known as oviducts) until they reach the uterus. If an egg is fertilised by a sperm, it implants in the uterus, where it will grow into a baby. See Where do babies come from? for more on this.
* Here we talk about the “female” body in a biological sense, but please note that gender depends on more than just your body – see our section on gender identity.